Name
Configuration — Common SAMA5D3 configuration options
Overview
Startup
The SAMA5D3 variant HAL package supports four separate startup types for application configuration:
- ROMRAM
This startup type is for stand-alone applications that are loaded into external DDR2-SDRAM via a second-level boot loader (e.g. the default SAMA5D3x-CM based AT91BootLoader, or the eCosPro
BootUploader), or via a JTAG/SWD hardware debugger. The data and BSS areas will be put into suitable memory locations as defined by the relevant platform HAL linker script. The application will be self-contained with no dependencies on services provided by other software. The eCos startup code will perform all necessary hardware initialization.![[Note]](pix/note.png)
Note The application is copied from its persistent location by the second-level application bootloader, or is directly loaded to RAM via a JTAG/SWD hardware debugger. The
ROMRAMstartup code does not perform the copy to RAM itself.- SRAM
-
This startup type is used for stand-alone
applications. The application will be loaded from a suitable supported
“bootable” device by the on-chip first-level
(
RomBOOT) bootloader, or directly via a hardware (JTAG/SWD) debugger. The application will be self-contained with no dependencies on services provided by other software. It is not envisaged that theSRAMstartup type will normally be used for full applications, primarily being used for developingRomBOOTloaded second-level bootloaders. However, it can be useful for small platform verification tests loaded via JTAG. - ROM
- This startup type is used for stand-alone applications which will be programmed into bootable memory located in the EBI_CS0 space from 0x10000000. The data and BSS areas will be put into suitable memory as defined by the relevant platform HAL linker script. The application will be self-contained with no dependencies on services provided by other software. The program expects to boot from reset with the EBI_CS0 space mapped from location zero. It will then transfer control to the 0x10000000 region. The eCos startup code will perform all necessary hardware initialization.
- RAM
This startup type is used for RAM based applications that are dependent on a “debug” monitor (e.g. RedBoot or GDB stubs) for some run-time services. By default the application will use the eCos virtual vectors mechanism to obtain services from the monitor, including diagnostic output. Normally arm-eabi-gdb is used to load a
RAMstartup application into memory, and then to debug it. It is assumed that the hardware has already been initialized by the relevant debug monitor.This startup type can be useful during development, since it allows debugging applications where a hardware debug solution is not available.
RedBoot and Virtual Vectors
If the application is intended to act as a ROM monitor, providing
services for other applications, then the configuration
option CYGSEM_HAL_ROM_MONITOR should be
set. Typically this option is set only
when Building RedBoot.
If the application is supposed to make use of services provided by a
ROM monitor, via the eCos virtual vector mechanism, then the
configuration option CYGSEM_HAL_USE_ROM_MONITOR
should be set. By default this option is enabled when building for
a RAM startup, and disabled otherwise.
If the application does not rely on a ROM monitor for diagnostic
services then, by default, the on-chip DBGU serial
port will be used for HAL diagnostic output.
RedBoot Location
RedBoot can be used in conjunction with the host
debugger arm-eabi-gdb to load and debug
applications configured for the RAM startup
type. Depending on the product requirements the RedBoot binary can
either be executed in-situ from the NOR flash, or loaded dynamically
into the DDR2-SDRAM for execution.
The ROMRAM
RedBoot diagram shows the memory layout for a RAM resident
RedBoot. The RedBoot binary is loaded into its final DDR2-SDRAM
location either via a second-level boot loader
(e.g. BootUp) or directly
using a hardware debugger.
![[Note]](pix/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
The addresses shown in the following diagrams are based on the default linker script values. |
Figure 287.1. ROMRAM RedBoot
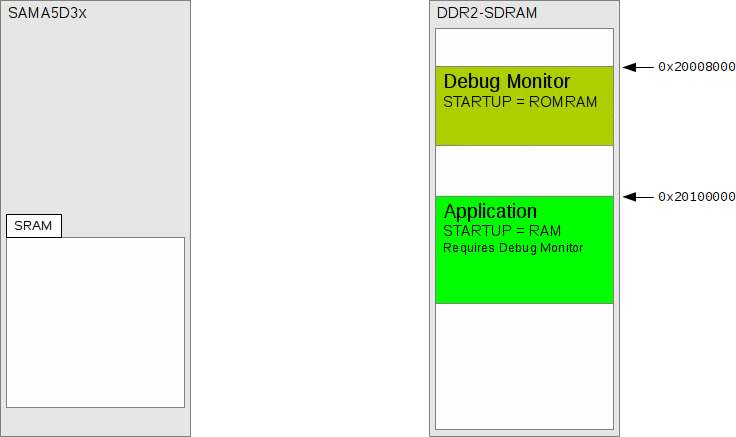
An illustration of a ROMRAM RedBoot executing from DDR2-SDRAM
Any application can be configured for the ROM
startup type, and when stored from offset 0 in the
NOR flash (mapped to address 0x10000000) the CPU
can be configured (via BMS_BIT=1) to execute the
code upon reset. The application does not need to be a debug monitor,
but can be the final application if required.
The ROM
RedBoot diagram shows the memory layout for a NOR flash
resident RedBoot.
Figure 287.2. ROM RedBoot
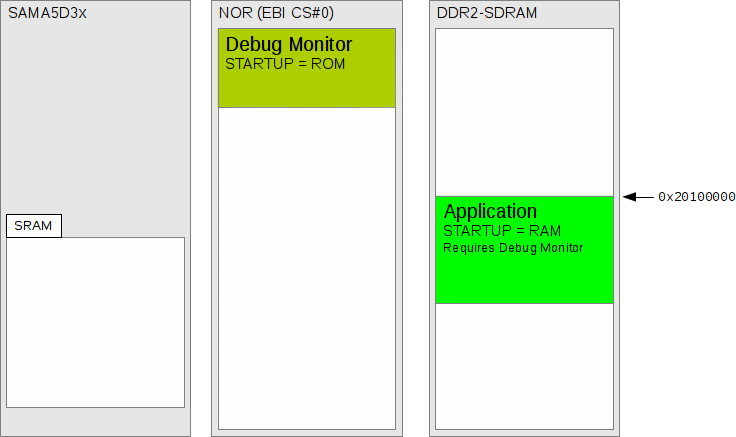
An illustration of a ROM RedBoot executing from NOR flash
| 2025-10-02 | eCosPro Non-Commercial Public License |



